Technology has brought with it good tidings, yet the transformations and the evolution it has caused in our lives and businesses are so rapid we can hardly keep tabs. Over the years, many approaches have been employed to solve the problems that humans and businesses face every day. Some of the problem-solving approaches that were considered most effective previously have not stood the test of time and can therefore not be applied to solve today’s complex problems and challenges. The fourth industrial revolution demands new and innovative ways of thinking that will deliver effective solutions that enhance business processes and service/product delivery. This largely involves design thinking.
Design thinking in itself is not new as it was practiced in the past to design and construct bridges, monuments, and other amenities and systems. However, design thinking has evolved over the years to be more innovative and consumer-centric to deliver effective solutions to complex problems. Today, a design thinking and innovation specialist is becoming more and more important across all business sectors to implement innovative non-linear design thinking approaches to drive expected results.
-
Table of Contents
Understand what design thinking is
Design thinking, as mentioned, is a non-linear iterative problem-solving technique that focuses on prioritizing the needs of the consumer. Design thinking specialists develop and test prototypes for products, systems, processes, and other solutions that meet consumer needs. This process is iterative, allowing solutions to be improved continuously to respond to consumers’ evolving needs.
Design thinking has been applied widely to tackle problems whose nature is ill-defined or unknown. Teams consider the needs of consumers, appropriate technology, as well as business objectives to develop effective concepts that will not only meet consumer needs but also drive business success.
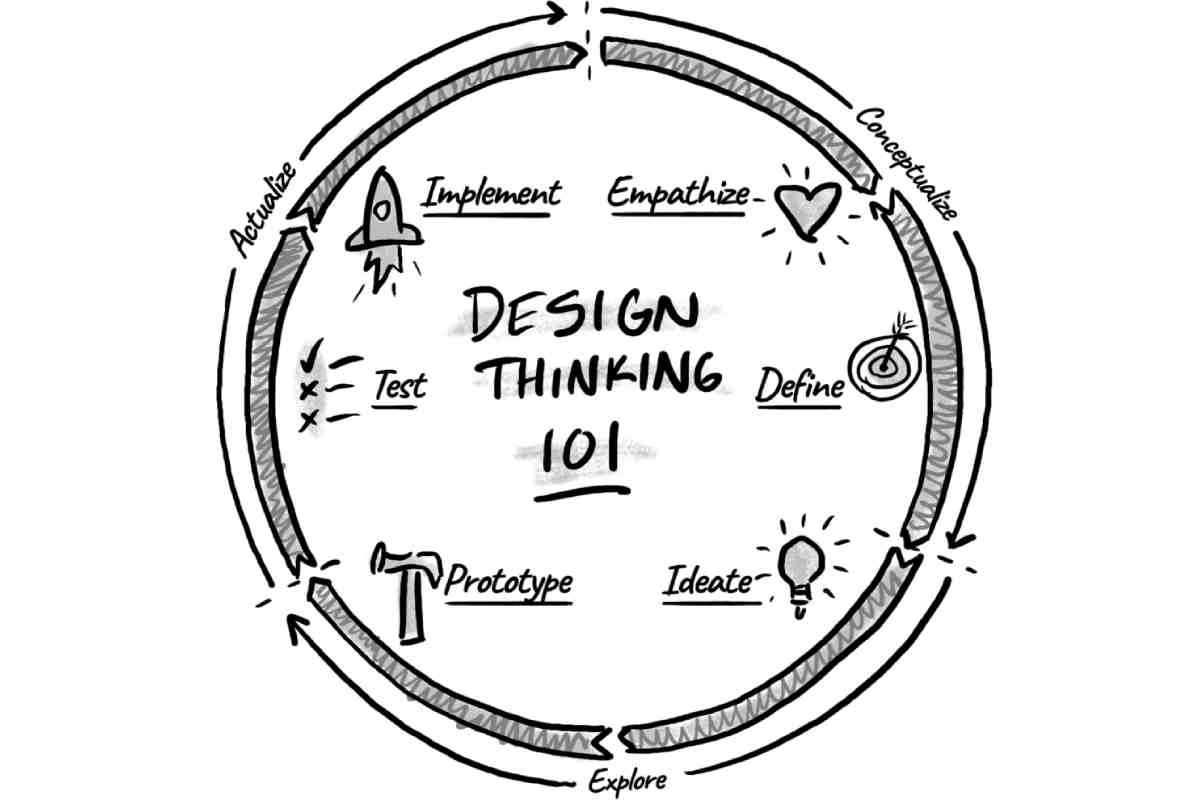
Design thinking starts from the point of observing how consumers interact with their environments, identifying their needs from their perspective, and then developing innovative solutions to meet these needs. It involves the following five phases:
- Empathize. The design thinking and innovation specialist researches and understands the needs and challenges that the target market experiences in the process of interacting with the organization’s products. Through empathy, they step into the shoes of the consumers to understand their experiences which helps them not just acquire information needed to design innovative solutions but also eliminate any assumptions.
- Define. The identified problem/challenge are synthesized to help define the problem in detail to get a comprehensive overview of the problem from various perspectives. A problem statement is formulated to guide the next phase.
- Ideate. In this phase, designers try to generate possible solutions to the problems/challenges through techniques like brainstorming, worst idea, questioning assumptions, and others. Here, the team gathers as many ideas as possible drawn from different skills, perspectives, and thinking styles of each member to try and capture aspects of the problem comprehensively.
- Prototype. From the ideas presented in the ideation phase, this stage allows designers to conceptualize and experiment with their ideas to validate them for the problem being tackled. This is done by modeling prototypes. Prototypes allow designers to test the effectiveness of the proposed solution, discover unanticipated implementation challenges, and refine the solution where necessary before it is designed and released to the market.
- Test. Testing prototypes involves exposing them to sample users to get their feedback on the practicability of the solution. Designers get to gain new insight and knowledge about their proposed solution, identify potential issues, refine it further to meet users’ needs.
-
Know the roles of design thinking specialists
Design thinking specialists are the professionals in the organization who possess an in-depth understanding of both existing and potential customers. They take time to observe customers as they interact with the organization’s products, identify the challenges the customers may be undergoing, and empathize with them to develop innovative solutions that will address the customer needs.
Design thinking and innovation specialists are depended upon to analyze consumer needs and continuously improve an organization’s products, services, and processes to meet these needs. What distinguishes these professionals from others is the fact that they are able to identify all the elements of consumer needs in detail and then apply their creativity to address them.
Some common roles of design thinking and innovation specialists are:
- Redefining the value of an organization’s products or services
- Researching, analyzing, and gathering information and insight on complex challenges affecting various groups of people to identify opportunities for business based on current trends, emerging technology, and customer insight
- They study evolving markets and consumer behavior and redefine business models to cater to the current markets and modern consumers.
- They develop systems that help the organization adapt faster to rapidly changing markets.
- They conduct needs assessments for existing customers to identify their challenges or unmet needs in the course of interacting with the organization’s products/services.
- Develop prototypes to validate the suitability of the organization’s products in new markets and help the organization scale.
- They identify problems from the unknown. Many times these problems are ill-defined and cannot be solved using only data.
-
Familiarize yourself with popular design thinking frameworks
Most design thinking frameworks have a common pattern when it comes to developing solutions for problems. Most are inclined towards empathy learning and understanding of customer needs, issues, or challenges; the gathering of insight; developing; and delivering solutions to address these needs. However, each framework is unique in process, tools, and focus.
-
IDEO
IDEO is a traditional design thinking approach that encompasses three stages including:
- Inspire
- Ideate
- Implement
This is a comprehensive human-centric design thinking approach founded on three principles, viability economically, desirability from the human perspective, and feasibility in terms of technology. IDEO can be implemented by both designers and professionals without a design background.
-
Heart, Head, and Hand
The heart, head, and hand design thinking model is a cognitive process of ideating solutions. It has its focus on communication in which the three elements are critical in this respective order.
- Heart. The designer connects with the user at heart (with empathy) to understand their issues and challenges from the consumer’s perspective.
- Head. The designer then expresses the desire to offer a befitting solution based on evidence from gathered information (head).
- Hand. The designer then gets down to creating the envisioned solution (hand).
-
HCD (Human-Centered Design)
The human-centered design approach to problem-solving, like the others, borders on developing empathy with the people for which a solution is being developed. Thus, a product, service, or solution should be developed to meet the core needs of its consumers. The acronym HCD was reinvented to mean hear, create, and deliver.
-
What X4
The what x4 design thinking model advanced by Jeanne Liedtka and Tim Ogilvie creates a problem-solving approach that asks the necessary questions commonly known as the 4 W’s:
- What is? Current situation
- What if? Ideation of possible solutions
- What wows? Working with users to know what will appeal to them.
- What works? Creating a balance between business objectives and meeting consumer needs.
There are many more design thinking models apart from the four that we have mentioned that are implemented for problem-solving that a designer who is launching his/her career can research.
-
Know and possess top skills required for design thinking
Some of the top skills required for design thinking are:
- Empathy
- Entrepreneurial initiative
- Questioning mindset that inspires conversations, understanding, and knowledge acquisition
- Innovation and creativity
- Communication, collaboration, and teamwork
- Customer orientation
- Systems thinking
- Agility and adaptivity for continuous improvement
- Leadership
- Change management
-
Get yourself into learning and acquiring credentials
Accomplished design thinking professionals agree that there is never an end to learning in design thinking as this process is iterative in nature and involves continuous improvement. Markets are evolving rapidly, and customer expectations are ever-changing; therefore, continuously satisfying customer needs demands continuous learning. However, the first step to launching your career in design thinking is to acquire the necessary credentials by taking a certification course with an accredited institution and using it to demonstrate your skills in your career.
Wrapping up
More than anything, designing is a human-centric approach to solving problems. It places humans at the center of the entire process and empathy as the most valuable element. This is because it takes stepping into the customer’s shoes to understand their experiences from their perspective and develop appropriate solutions. Design thinking has been used across most sectors to drive desired results. A successful product or effective solution is one that addresses the needs of the consumer to build wonderful experiences.